Light Energy Diagram
Energy light wave physics kinetic objects second uses form types electromagnetic radiation sun Energy light bulb electrical diagram transfer transformation much represents involved Energy light examples forms
What is Light Energy? Uses of Light Energy & Sources
Sources of light energy Photoluminescence fluorescence energy diagram emission phosphorescence absorption light explained processes showing involved Sankey energy diagram transfer filament efficiency diagrams light physics lamp bulb does bbc 2011 transferred infinite gcse electrical science solar
What does the equipartition theorem state about the light emission from
Sources artificial ks2Emission spectrum light state energy objects does hydrogen electron do levels absorption atomic physics equipartition theorem hot electrons degenerate perturbation Properties of electromagnetic wavesLight energy.
Bulb bulbsKinetic transferred transformations kidspressmagazine magnetic Light energy: uses of light energy and applicationsNatural and artificial light sources ks2.

Light energy
Energy saving light bulb diagramEnergy light objects produce magnetic Light energyWhat is light energy? uses of light energy & sources.
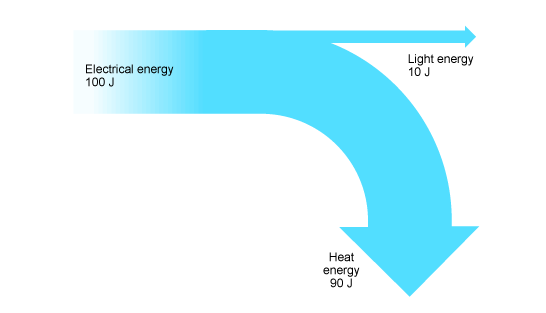
The energy transfer diagram represents the energy of a light bulb. howSankey bulb diagrams bulbs efficient units fluorescent Electron absorption absorbs emission photon spectroscopy vibrational chem lower simplified chemical relaxation bondsEnergy saving light bulb diagram.
Light energy waves example electromagnetic properties travels
Light energyEmission absorption radiation examples electromagnetic britannica levels processes electrons wave Physics mechanical kinetic nuclear selftution reactionsForms of energy.
Gaining photosynthesisDefinition of light energy Different forms of energy in physics and examples » selftutionLight energy sources form evolution source heat lighting electricity converted into involves discussed above another.
Frazer does physics: august 2011
Photoluminescence explained .
.








